- Home
- Tutorial
- Resource Guides
- Focus Areas
- LSF Programs
-
Professional
Development - Review Process
-
A project of LSF

Search for Resources
Description
Understanding Sustainable Living is part of the World's Largest Lesson, which brings the Global Goals to children all over the world and unites them in taking action. In this sixty minute lesson, students will:
- listen to the song "Electric Car" by They Might be Giants and use the song to make their definition of the word sustainability
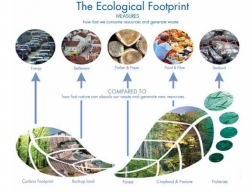
- discuss if they think their life is sustainable and how they can adjust their lifestyles. This should lead students to the idea of Ecological Footprints
- read the story of a student in another country and use the online tool to calculate that student's Ecological Footprint
- make up a collective bar graph (or table) of the student's Ecological Footprint and summarize their character's lifestyle
- discuss differences in their character's lifestyles and how that affects their Ecological Footprint and what lifestyle changes could we make to have the biggest change in our Ecological Footprint
At the end of this lesson, students will be able to explain the concept of sustainability, evaluate various lifestyle choices for sustainability using an online ecological footprint calculator to real-life data, and identify actions students can take to make their lifestyle more sustainable.
General Assessment
What skills does this resource explicitly teach?
This resource explicitly teaches students how to analyze one's ecological footprint using either an online tool or a written quiz.
Strengths
- This resource has a detailed lesson plan for teachers with clear goals
- All materials needed by the students are available and ready to print in the appendix
- This resource is available in both official languages
- Alternatives and differentiation ideas are provided for all activities based on students level
- Background information on the topic is provided for teachers
Weaknesses
- Evaluation tools are not provided in this resource
- This resource does not provide students a chance to place into action their ideas of sustainability
Recommendation of how and where to use it
Since this resource is only one lesson, it would be a great addition to any larger discussion of human impact and ecological footprints.
Relevant Curriculum Units
The following tool will allow you to explore the relevant curriculum matches for this resource. To start, select a province listed below.
- Step 1Select a province
- Alberta
- Step 2Select a grade level
- Grade 6
- Step 3Select a subject
- Math
- Step 4Relevant matches
- Statistics: The science of collecting, analyzing, visualizing, and interpreting data can inform understanding and decision making.
- Grade 8
- Step 3Select a subject
- Math
- Step 4Relevant matches
- Knowledge and Employability: Statistics and Probability
- Statistics and probability
- Grade 9
- Step 3Select a subject
- Math
- Step 4Relevant matches
- Knowlege And Employability: Statistics and Probability
- British Columbia
- Step 2Select a grade level
- Grade 6
- Step 3Select a subject
- Math
- Step 4Relevant matches
- Data from the results of an experiment can be used to predict the theoretical probability of an event and to compare and interpret
- Grade 9
- Step 3Select a subject
- Science
- Step 4Relevant matches
- Science 9: The biosphere, geosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere are interconnected, as matter cycles and energy flows through them.
- Manitoba
- New Brunswick
- Step 2Select a grade level
- Grade 6
- Step 3Select a subject
- Math
- Step 4Relevant matches
- Statistics and Probability
- Social Studies
- Step 4Relevant matches
- Cultures
- Empowerment: Economics
- Atlantic Canada and the World:
- Newfoundland & Labrador
- Step 2Select a grade level
- Grade 6
- Step 3Select a subject
- Math
- Step 4Relevant matches
- Statistics & Probability
- Social Studies
- Step 4Relevant matches
- World Issues
- Northwest Territories
- Step 2Select a grade level
- Grade 6
- Step 3Select a subject
- Math
- Step 4Relevant matches
- Data from the results of an experiment can be used to predict the theoretical probability of an event and to compare and interpret
- Grade 9
- Step 3Select a subject
- Science
- Step 4Relevant matches
- Science 9: The biosphere, geosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere are interconnected, as matter cycles and energy flows through them.
- Nova Scotia
- Step 2Select a grade level
- Grade 6
- Step 3Select a subject
- Math
- Step 4Relevant matches
- Statistics and Probability
- Science
- Step 4Relevant matches
- Science 6: Electricity
- Social Studies
- Step 4Relevant matches
- Social Studies 6: World Issues
- Nunavut
- Step 2Select a grade level
- Grade 6
- Step 3Select a subject
- Math
- Step 4Relevant matches
- Statistics and Probability
- Grade 8
- Step 3Select a subject
- Math
- Step 4Relevant matches
- Knowledge and Employability: Statistics and Probability
- Grade 9
- Step 3Select a subject
- Math
- Step 4Relevant matches
- Knowlege And Employability: Statistics and Probability
- Ontario
- Prince Edward Island
- Step 2Select a grade level
- Grade 6
- Step 3Select a subject
- Math
- Step 4Relevant matches
- Statistics and Probability
- Social Studies
- Step 4Relevant matches
- World Issues
- Quebec
- Saskatchewan
- Yukon Territory
- Step 2Select a grade level
- Grade 6
- Step 3Select a subject
- Math
- Step 4Relevant matches
- Data from the results of an experiment can be used to predict the theoretical probability of an event and to compare and interpret
- Grade 9
- Step 3Select a subject
- Science
- Step 4Relevant matches
- Science 9: The biosphere, geosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere are interconnected, as matter cycles and energy flows through them.
Themes Addressed
Citizenship (2)
- Ecological Footprint
- Sustainable Consumption
Energy (1)
- Alternative Energy
Sustainability Education Principles
| Principle | Rating | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Consideration of Alternative Perspectives | Very Good | Throughout this lesson, students get to form their own opinions and take informed positions based on the information they will be provided. |
Consideration of Alternative Perspectives:
| ||
| Multiple Dimensions of Problems & Solutions | Good | While analyzing the ecological footprints in the story pack, students understand how the social, economical and environmental dimensions are connected. |
| Multiple Dimensions of Problems & Solutions: Effectively addresses the environmental, economic and social dimensions of the issue(s) being explored.
| ||
| Respects Complexity | Very Good | |
| Respects Complexity: The complexity of the problems/issues being discussed is respected. | ||
| Acting on Learning | Satisfactory | Even though this resource does not provide explicit activities for working towards change, it gives students a good idea of how they could reduce their ecological footprint. It would be easy for the teacher to extend this activity by asking students to choose one action to reduce their footprint. |
| Acting on Learning: Learning moves from understanding issues to working towards positive change — in personal lifestyle, in school, in the community, or for the planet
| ||
| Values Education | Very Good | Students opinions are at the base of this resource. Students are asked to share their opinions in discussion throughout this lesson. |
| Values Education: Students are explicitly provided with opportunities to identify, clarify and express their own beliefs/values. | ||
| Empathy & Respect for Humans | Poor/Not considered | Not considered in this resource. |
| Empathy & Respect for Humans: Empathy and respect are fostered for diverse groups of humans (including different genders, ethnic groups, sexual preferences, etc.). | ||
| Personal Affinity with Earth | Good | Throughout this lesson, students will discover how our actions effect our environment and therefore foster an appreciate for the natural world. |
| Personal Affinity with Earth: Encourages a personal affinity with -the natural world.
| ||
| Locally-Focused Learning | Satisfactory | In this lesson, students will need to analyze the ecological footprint of fictional characters. Through this, they will most likely think about their own footprint and therefore it will be relevant to them. |
| Locally-Focused Learning: Includes learning experiences that take advantage of issues/elements within the local community.
| ||
| Past, Present & Future | Good | |
| Past, Present & Future: Promotes an understanding of the past, a sense of the present, and a positive vision for the future. | ||
Pedagogical Approaches
| Principle | Rating | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Open-Ended Instruction | Very Good | With the number of discussions embedded in this lesson, students are not steered toward one right answer. |
| Open-Ended Instruction
: Lessons are structured so that multiple/complex answers are possible; students are not steered toward one 'right' answer. | ||
| Integrated Learning | Good | It is clear that some Science outcomes, in terms of ecological footprints, and some Math outcomes, with some data collection and analysis, are covered in this resource. |
| Integrated Learning: Learning brings together content and skills from more than one subject area
| ||
| Inquiry Learning | Satisfactory | |
| Inquiry Learning: Learning is directed by questions, problems, or challenges that students work to address.
| ||
| Differentiated Instruction | Very Good | Ideas for differentiation and alternative activities are provided for each learning activity. |
| Differentiated Instruction: Activities address a range of student learning styles, abilities and readiness.
| ||
| Experiential Learning | Satisfactory | Students have the chance to use an online tool to calculate one's ecological footprint. |
| Experiential Learning: Authentic learning experiences are provided
| ||
| Cooperative Learning | Satisfactory | Students will need to work in groups. |
| Cooperative Learning: Group and cooperative learning strategies are a priority.
| ||
| Assessment & Evaluation | Poor/Not considered | No assessment tools are provided in this resource. |
| Assessment & Evaluation: Tools are provided that help students and teachers to capture formative and summative information about students' learning and performance. These tools may include reflection questions, checklists, rubrics, etc. | ||
| Peer Teaching | Satisfactory | Students will give a small presentation on their fictional character's ecological footprint. |
| Peer Teaching: Provides opportunities for students to actively present their knowledge and skills to peers and/or act as teachers and mentors.
| ||
| Case Studies | Poor/Not considered | |
| Case Studies: Relevant case studies are included. Case studies are thorough descriptions of real events from real situations that students use to explore concepts in an authentic context. | ||
| Locus of Control | Good | |
| Locus of Control: Meaningful opportunities are provided for students to choose elements of program content, the medium in which they wish to work, and/or to go deeper into a chosen issue. | ||